Contextual Bandit Methodology
Methodology
This page covers the high level approach that Statsig takes to running contextual bandits across cloud and warehouse native. Specifics of implementation change frequently as we experiment and optimize our approaches, so this documentation is deliberately high level.
Core Approach
What is implemented in Statsig is close to the the disjoint model methodology from Li, Chu, Langford, Schapire. In short, several models are trained - one per variant - and their estimate CIs modelled. When the contextual autotune is triggered, the latest version of the model is used to estimate the user's outcome, plus the upper end of the 95% CI for the estimate.
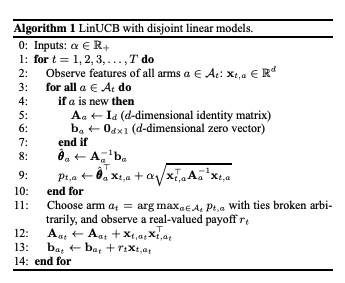
In the case of categorical outcomes, this is modelled as a logistic regression with l2 penalty. In the case of a continuous outcome space, this is modelled as a multivariate ridge regression.
Training Data and Sampling
To keep data relevant, contextual autotune data is preferentially upsampled for recent dates. Specifically there are two mechanisms for sampling:
- A flat number of samples, preferring most recent records, are selected
- Per day, in the last two weeks, samples are chosen to prefer more recent records
- Samples from the explore dataset are strictly preferred, but non-explore data may be chosen after to satisfy sample requirements. Records are then prioritized by a unit-ID hash to maintain stability in the training set between subsequent runs and avoid major jitter
- A sample set is chosen per-variant using this methodology to avoid bias from a model dominating the space and therefore being overrepresented in training data
This means that if a model has very low volume, it will have low representation in the training data; this causes higher CIs and makes the sample more likely to be selected due to the upper bound being increased by merit of its rarity and acts as a mechanism for bounce-back.
Model and Feature Updates
Models are updated hourly. If a model definition (features or target outcome change), the data will be fully reset, functionally resetting and retraining the model to match the new definition on the next hourly update.
The pre-training data pipeline is available in the history view on the results page, showing the SQL used and caching tables where data is stored. This allows users to easily use the same data to validate or explore modeling approaches.
Feature Encoding
Features with numerical-only values are treated as continuous RVs. All others are string-encoded and one-hot-encoded into binary variables for regression, using the top 25 levels available in the data which have >1% coverage in the dataset.
This does mean that using an array of categories or tags does not work, or will encode the most common tagsets. The tagset needs to be provided as individual key-value pairs in the user custom object.
Model Monitoring
Currently, there are not diagnostics for model characteristics over time. The model coefficients are visible in the results tab, and a view comparing performance between naive, random traffic and the targeted traffic is available for understanding if the model's performance relative to blind allocation improves or degrades over time.